Melamine is an organic compound used in door manufacturing. It is an industrial chemical widely utilized in plastics production. If it is combined with formaldehyde it strengthens as it is heated. It contains 66% of nitrogen by mass. Melamine (density: 1,57 g/cm³) decomposes at its melting point of 345 °C. It is soluble in water. Melamine-faced panels are manufactured by bonding melamine onto MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) boards applying heat and pressure. Such panels are utilized in melamine-faced door production. Melamine-faced doors vary in color and pattern design. Melamine-faced door leaves are made of three main components. Finger-joint wood spars which form the main frame of the door leaf are made of spruce or fir tree. They are 42 mm wide and 35 mm thick. Spars have a moisture content stabilized at 10-14%. Additional spars are used for reinforcement at handle, lock and hinge points.
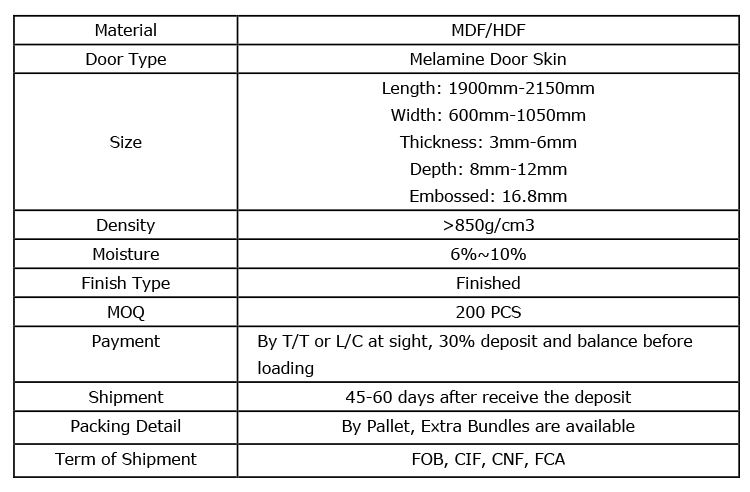
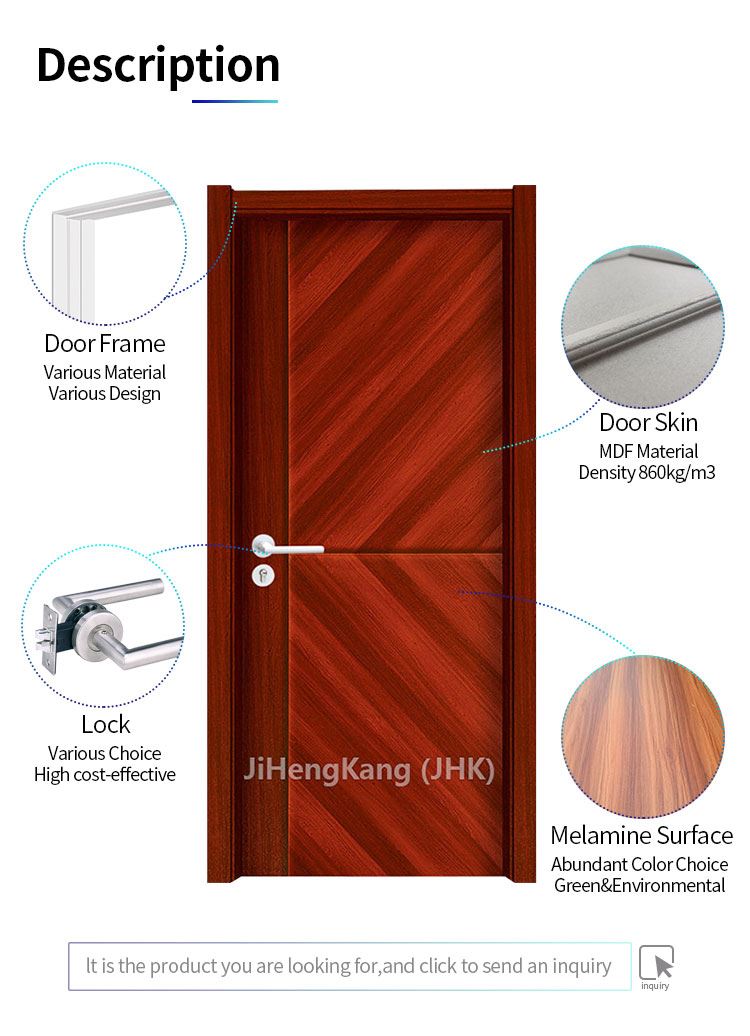
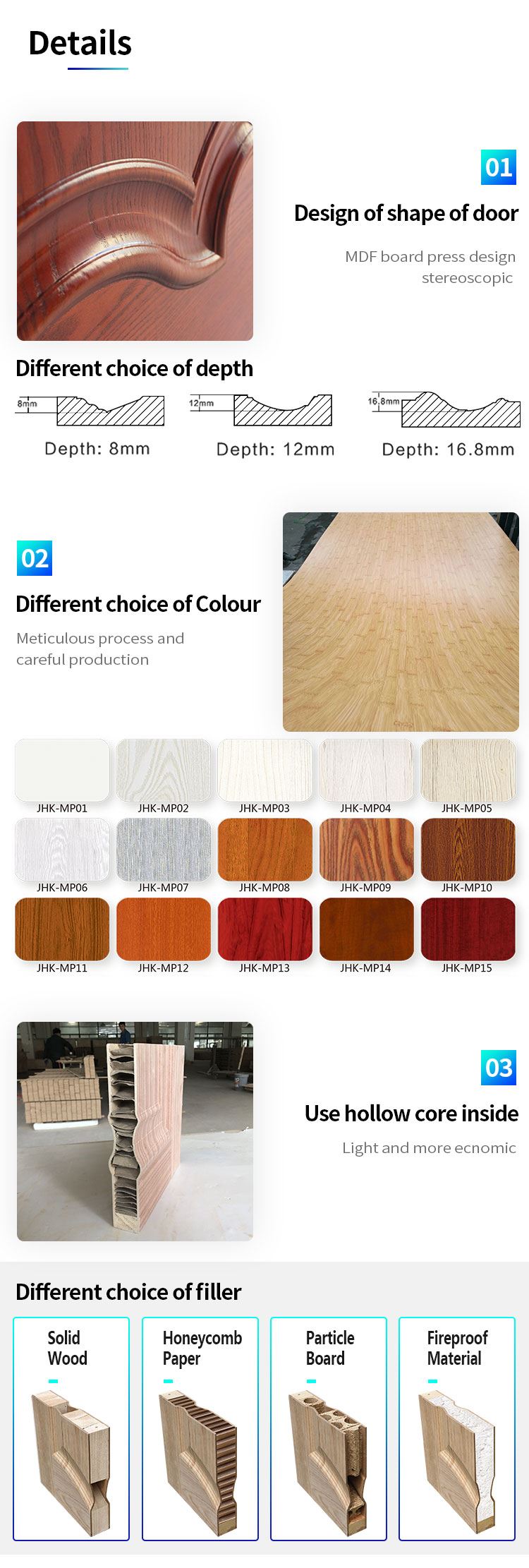
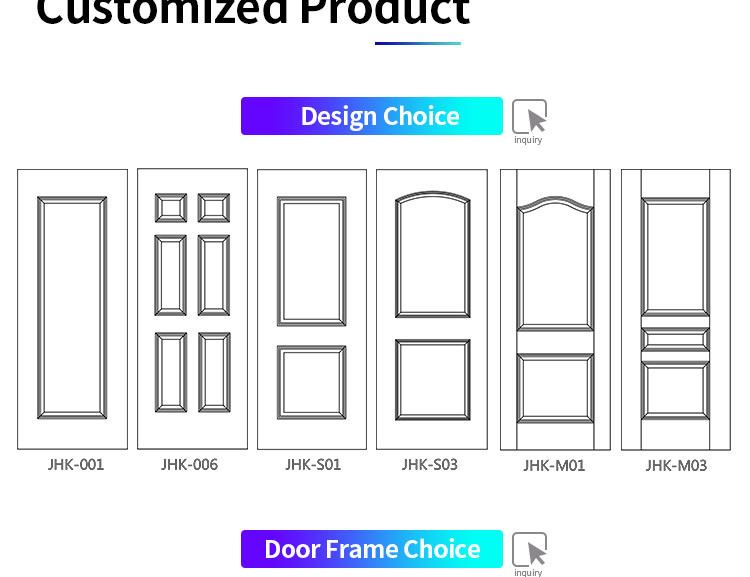





Melamine is an organic compound used in door manufacturing. It is an industrial chemical widely utilized in plastics production. If it is combined with formaldehyde it strengthens as it is heated. It contains 66% of nitrogen by mass. Melamine (density: 1,57 g/cm³) decomposes at its melting point of 345 °C. It is soluble in water. Melamine-faced panels are manufactured by bonding melamine onto MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) boards applying heat and pressure. Such panels are utilized in melamine-faced door production. Melamine-faced doors vary in color and pattern design. Melamine-faced door leaves are made of three main components. Finger-joint wood spars which form the main frame of the door leaf are made of spruce or fir tree. They are 42 mm wide and 35 mm thick. Spars have a moisture content stabilized at 10-14%. Additional spars are used for reinforcement at handle, lock and hinge points.











